Gas use in vehicles
Data as per the 2020 Annual Report
Gazprom Gazomotornoye Toplivo – a sole operator company focused on expanding the use of natural gas as a vehicle fuel
Photo essay
Video
The media content cannot be displayed because you did not consent to the use of cookies by gazprom.com.
You can give consent to store cookies right now or do it later in your settings.
The media content cannot be displayed because you did not consent to the use of cookies by gazprom.com.
You can give consent to store cookies right now or do it later in your settings.
The media content cannot be displayed because you did not consent to the use of cookies by gazprom.com.
You can give consent to store cookies right now or do it later in your settings.
Strategy
The production and marketing of compressed and liquefied natural gas as a vehicle fuel rank among Gazprom’s top priorities. Gazprom Gazomotornoye Toplivo, a special-purpose company, was set up as part of the systematic efforts to develop the natural gas vehicle (NGV) market.
Exceptionally economical and eco-friendly
Natural gas is the most economical, eco-friendly and safe type of fuel available today. It is essentially a ready-to-use vehicle fuel, which makes it much cheaper than gasoline and diesel fuel. Moreover, the engines of gas-fueled vehicles comply with the highest emission standards, Euro 5 and Euro 6. According to the Russian Emergencies Ministry’s classification, natural gas belongs to the category of the least dangerous flammable substances.
Two types of natural gas are used as a vehicle fuel: compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG).
The target market segments for the fuel are as follows:
- CNG – passenger and light cargo transport, motor cars and municipal vehicles;
- LNG – line-haul cars, railway and waterborne transport, quarry machinery and agricultural equipment.
Russian NGV market
The use of natural gas as a vehicle fuel is steadily increasing in Russia.
The Russian NGV market has a considerable capacity for growth, which is facilitated by:
- immense natural gas reserves and a well-developed gas distribution network providing for reliable supplies of gas as a vehicle fuel in the long term;
- introduction of energy-efficient fuels in transport, including via conversion of passenger and municipal vehicles to natural gas in the cities with over 100,000 people;
- growing variety of natural gas-fueled equipment and the expanding gas filling infrastructure;
- low price of natural gas compared to conventional vehicle fuels.
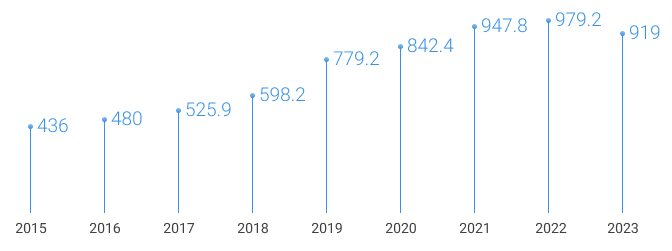
As of December 31, 2023, there were 464 operational CNG filling stations with a total annual capacity of over 3.3 billion cubic meters owned by the Gazprom Group and Gazprom Gazomotornoye Toplivo in Russia.
In 2023, Gazprom sold 919 million cubic meters of CNG through its refueling network.
NGV infrastructure development
The existing NGV refueling network of Gazprom and Gazprom Gazomotornoye Toplivo covers 64 constituent entities of the Russian Federation in eight federal districts.
In conjunction with the Federal Road Agency, the General Layout for gas filling infrastructure on federally maintained roads was developed. The Layout provides for the creation of a core network of 181 facilities by 2030 and the establishment of so-called NGV corridors on key existing and planned highways across Russia.